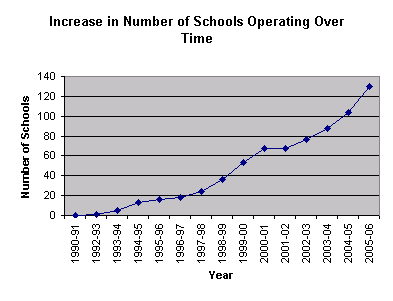
| School Year |
Schools Operating |
Legislative Changes |
| 1990-91 |
0 |
First charter law passed; district only chartering; limit of 8 schools |
| 1992-93 |
1 |
Cap raised to 20 schools; appeal to state board added |
| 1993-94 |
5 |
Cap raised to 35 schools |
| 1994-95 |
13 |
Public college sponsorship (up to 3 schools); overall cap raised to 40 schools; transportation revenue added |
| 1995-96 |
16 |
Compensatory (low income student) aid added |
| 1996-97 |
18 |
All caps removed; private college sponsors added; lease aid/start-up aid added |
| 1997-98 |
24 |
Intermediate district sponsors added; lease aid increased |
| 1998-99 |
36 |
Integration/referendum aids added; lease aid increased |
| 1999-00 |
53 |
Non-profit organization and foundation sponsors added; sponsors allowed to charge schools for oversight role |
| 2000-01 |
67 |
New provisions regarding conflicts of interest, financial management training and audit requirements added, state charter school advisory committee created |
| 2001-02 |
67 |
Mainly technical changes |
| 2002-03 |
77 |
Advisory board role changed; conditions set for expanding sites or adding grades; teacher leaves from districts limited to five years; Lease aid and start-up aid reductions |
| 2003-04 |
88 |
Proposals for additional sponsors; building ownership; extra-curricular access; making teacher majority optional |
| 2004-05 |
104 (est) |
Ongoing efforts will be needed to meet ongoing legislative goals — particularly around equitable funding and annual appropriations for facilities and start-up aid, as well as efforts, as needed, to repel proposals to limit the growth and autonomy of charters |
| 2005-06 |
130 (est) |
Longer-range issues will also include creatively addressing the facilities needs of charters, creating new ways of organizing and financing extra-curricular activities, creatively addressing transportation and distance learning challenges and opportunities, financing the role of sponsors and encouraging more proactive chartering by districts |